What Is Copra?
Copra is the dried meat, or kernel, of the coconut. It has a maximum moisture content of six percent. Derived from the coconut palm, copra is the chief commercial product from coconut, used mainly as a source of coconut oil. The remaining by-product, known as copra cake or copra meal, is used in blending livestock feed for its oil, protein, and carbohydrates, or as a raw material for the extraction of remaining oil by solvent extraction method. We can supply coconut oil production line for you.
How to Make Copra by Drying?
Copra can be made by smoke drying, sun drying, or kiln drying. Sun drying requires little more than racks and sufficient sunlight. After immersed in clean, cold water to wash away any adhering material, drained coconut halves are placed on the ground or racks with the open side turned to the sun. After two days, the kernel gets detached from the shell and can be removed. The detached kernels are set to dry again for a further period of four to five days. Sun drying is often combined with drying in a kiln. Coconut meat can also be dried using direct heat and smoke from a fire, using simple racks to suspend the coconut. The major producing country of copra is the Philippines. It is also an important export in Papua New Guinea, Solomon Islands, Vanuatu, Mozambique, Malaysia, and the Pacific Islands.
How to Press Coconut Oil From Copra?
As an oil-rich pulp, copra normally has an oil content varying from 65 to 72 percent. The quality of coconut oil is related to the quality of copra. The oil content of copra and the oil extraction rate vary according to the variety of coconut processed, its degree of ripeness, and growing conditions. The physical characteristics of copra which affect the oil quality and the extraction rate include the rubberiness of the meat, case hardening which results from inadequate drying, or charring of the meat from over-heating.
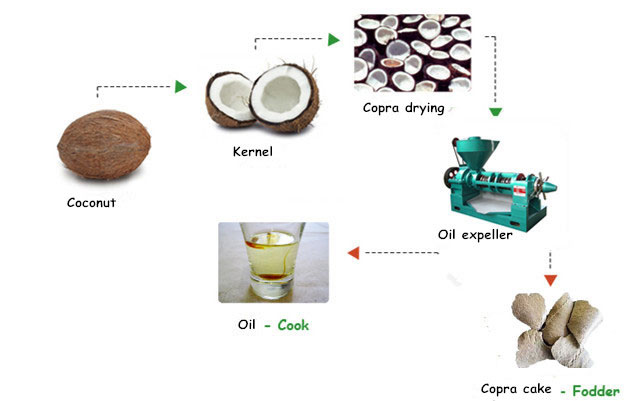
Oil extraction from copra is dry processing, different from the wet process which deals with fresh coconut meat. Crude coconut oil is processed from copra by two methods: mechanically by expeller pressing copra which have a high oil content, and solvent extraction for oil seeds with low oil content or for further oil extraction from copra cake. The residual of solvent extraction is called copra meal. For mechanical pressing, well-dried copra is cleaned and then cut into small chips. After proper cooking, it is fed into the expeller continuously and pressed twice, and then filtered by means of an oil filter. Screw oil press is such an expeller that process copra into coconut oil. It could process copra from 1 ton per day to 18 ton per day but only take about 1-2m ² area. The oil left in the cake is less than 6%. And cake thickness can be adjusted.
Applications of Coconut Oil
Coconut oil made from copra has good applications in the industrial area. It is used in the manufacture of toilet soap and laundry soap because it has high levels of lauric acid, an ingredient that gives the soap a quick-lathering property. Coconut oil is also used for manufacturing detergents, surfactants, emulsifiers, plasticizers and various other organic products which are bio-degradable.