Introduction of Deacidification System of Crude Oil Refinery Plant
The deacidification system of crude oil refinery plants is to remove free fatty acids(FFA) from pressed or extracted crude oil. Since FFA would produce an irritating odor and accelerate the hydrolysis rancidity rate of neutral oil, deacidification is necessary and it has long been used as the greatest economic benefit for the crude oil refining process, and the removal of FFA from crude oil is also the most difficult process in the crude oil refinery plant. If the process is mature enough, deacidification could achieve the effects of removing irritating odor, inhibiting oxidative rancidity, enhancing the physical and chemical stability of the oil, and determining the quality of the final oil product.
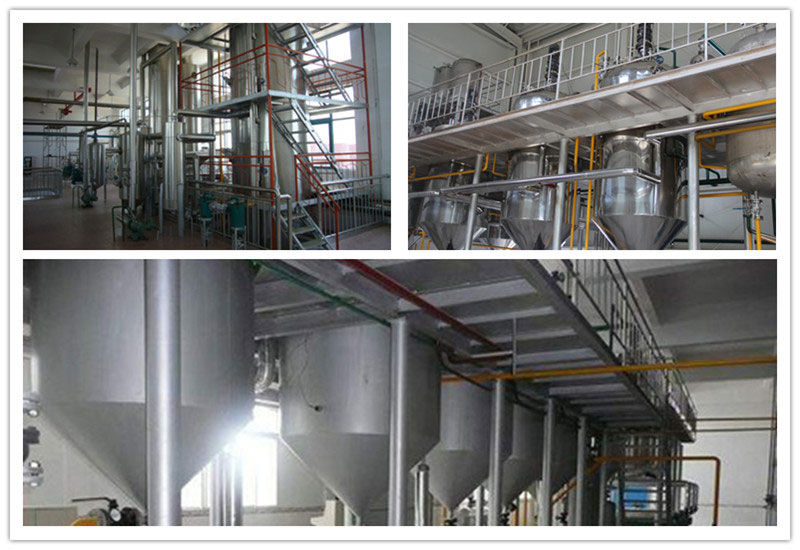

Common industrial deacidification methods are alkali refining (chemical deacidification method), steam distillation (physical deacidification method) and solvent extraction (mixed deacidification method), the most widely used methods are alkali refining system and steam distillation method.
Alkali Refining Process
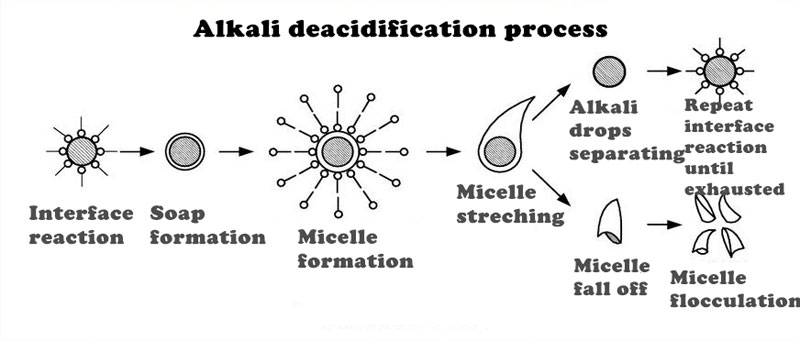 Alkali refining for removing acid is the most critical step in the entire refining process, and it creates conditions for decolorizing, deodorizing, hydrogenating, and deep processing of oil. After alkali refining, oil quality is improved, oil stability is increased and its storage time is prolonged. The Alkali refining method uses alkali to neutralize FFA in the oil to generate soap and the generated soap can adsorb impurities. Soap and impurities are then subsided and separated from the oil by gravitational sedimentation separation method or by centrifuge. Alkali refining is divided into the intermittent type and continuous type, and the intermittent type is suitable for concentrated alkali refining at low temperatures with steps like pre-treatment→lye neutralization→separation of soap stock→washing separation→dehydration(dissolution)→filtration→soap stock processing→packing.
Alkali refining for removing acid is the most critical step in the entire refining process, and it creates conditions for decolorizing, deodorizing, hydrogenating, and deep processing of oil. After alkali refining, oil quality is improved, oil stability is increased and its storage time is prolonged. The Alkali refining method uses alkali to neutralize FFA in the oil to generate soap and the generated soap can adsorb impurities. Soap and impurities are then subsided and separated from the oil by gravitational sedimentation separation method or by centrifuge. Alkali refining is divided into the intermittent type and continuous type, and the intermittent type is suitable for concentrated alkali refining at low temperatures with steps like pre-treatment→lye neutralization→separation of soap stock→washing separation→dehydration(dissolution)→filtration→soap stock processing→packing.
Features of Oil Deacidification System of Crude Oil Refinery Plant
- The machine capacity is customized according to your requirements.
- Oil deacidification machines can be flexibly worked with the entire oil refining line or can be used alone.
- The machine is made of food-grade stainless steel with polishing treatment, the materials are not stained or damaged.
- The deacidification tank is controlled by an electrical box, simple and safe operation. The customer can operate the machine well after video training.
Main Equipment of Oil Alkali Deacidification
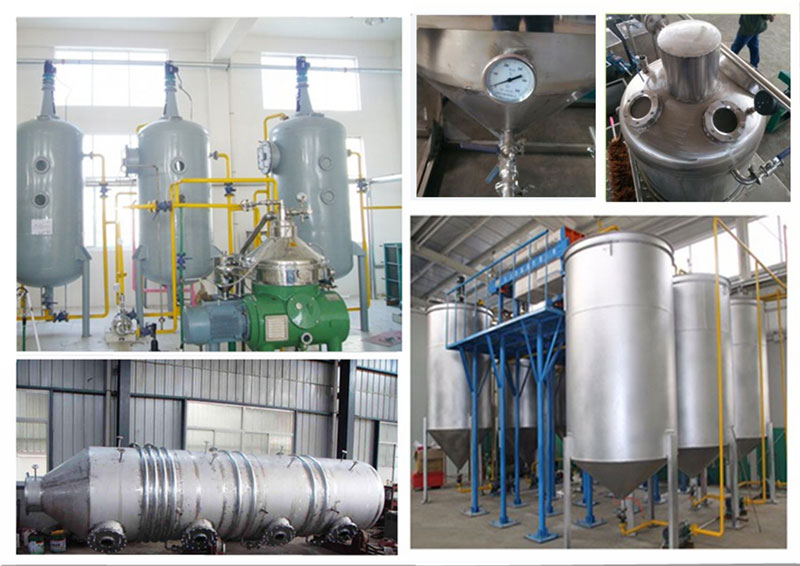

- Soap blending tank
- Oil and alkali proportioning device
- Mixing machine: ① blade mixer; ② centrifugal mixer; ③ static mixer.
- Centrifuge: ① tube centrifuge; ② disc centrifuge²
Disc centrifuge is mainly made up of the fuselage, drum, transmission, and water distribution devices. The mixture enters the drum from the bottom or top, then enters the discs from the dispensing holes in the lower and middle discs, and slides towards the inner wall of the drum, after that, the mixture is diluted by the flushing water come from the lower dispenser. And along the inner wall of the drum up into a centripetal pump in pump area, under the action of the centripetal pump the heavy material is discharged to the heaviest phase outlet, while the light material is discharged from light phase outlet.

Working Steps of Deacidification
-
Pre-treatment:
Filtering crude oil impurities to make it less than 0.2%. After mixing with acid, the acid value of the oil is measured by sampling.
-
Neutralization:
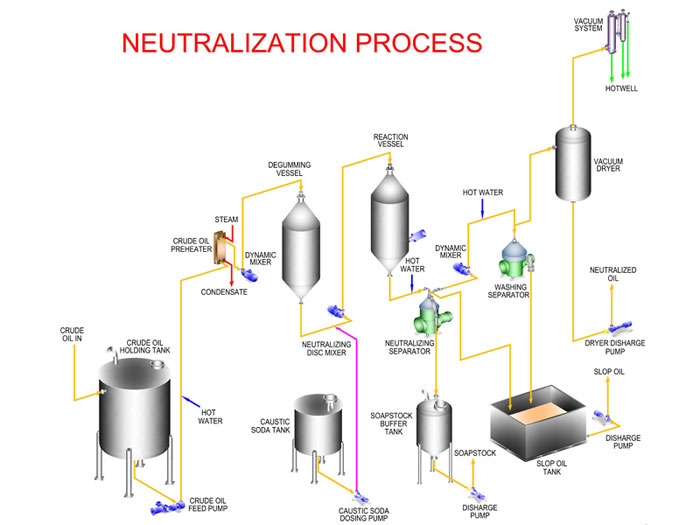
The neutralization reaction takes place in the reaction vessel. Its working principle is: the crude oil is pumped firstly from the oil holding tank to the heater for warming up to 20~40℃, then the heated, degummed oil is pumped to the mixer and mixed with phosphoric acid or citric acid for changing nonhydrated phospholipid into hydrated phospholipid in oil. After that, the oil is sent to the reaction vessel and reacts with 16~24°Be’ lye(around 0.05%~0.2% of the oil weight) within 5~10 minutes and the mixing speed is 60~70 r/min. After 20~50 minutes, when the oil and flocculent soap are significantly separated, reduce the stirring speed to 30 r/min and heat the oil by steam at the speed of 1℃/min to accelerate soap flocculating.
Please note: ensure that the final temperature is controlled at 60~65℃. Next, the upper oil is filtered to the washing equipment, while the soap stock is settling at the bottom of the barrel.
-
Separation of soap stock:
After neutralization, the settling soap would be discharged by pipe to the soap stock buffer tank. When the soap stock contains more oil, stop discharging soap stock and pump them into the soap stock tank for refining. After refining, the remaining oil from soap can be reused in next process.
-
Washing separation:
The deacidified oil still contains a few soap and to remove the residual soap, process water would be pumped into the oil with water temperature 3~5℃ higher than the oil. Each time the added water amount is 10%~15% of the oil volume and the washing process can be operated 1~3 times, then stirring well and keeping still for half an hour to one hour. Then, re-mixed oil and water are conveyed into the separator and the wastewater with soap impurities are separated and discharged to the slop oil tank.
-
Dehydration(desolution)
The washed oil still contains moisture and the moisture will affect oil stability, so the oil would be sent to the vacuum drier to remove moisture, and then the dehydrated water can be conveyed for the further process like decoloring, deodorizing, etc.
Please note: the extracted oil contains the solvent which can be removed by the first evaporating solvent to achieve an oil content of 50%, followed by hydrating and solvent removal.
-
Filtration and packaging
Finally, filtrate the dehydrated oil again for removing the residual impurities and package the oil in sealed barrels for low temperature, drying preservation.
Functions of Alkali Deacidification
The alkali which can neutralize FFA are sodium hydroxide(also known as caustic soda, NaOH), sodium carbonate(also known as soda ash, Na2CO3) and calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)2). In the oil industry, the commonly used ones are caustic soda and soda ash; or soda ash is used firstly, and then is caustic soda. In particular, caustic soda is the most widely used alkali at home and abroad. The main functions of alkali deacidification process can be summarized as the following points:
First, caustic soda neutralizes most of the free fatty acids in the crude oil. The resulting sodium aliphatate(sodium soap) and water are not easy to dissolve in the oil and become a flocculate and settle down.
Second, the neutralized sodium soap is a surface active material with a strong absorption capacity. Therefore, a considerable amount of other impurities(such as proteins, mucilaginous substances, pigments, phospholipids and substances with a hydroxy or phenolic) can also be absorbed into the sediments, and even the floating solid impurities can be entrained with the flocculent soap. So alkali refining has multiple functions of deacidification, degumming, removing solids impurities and bleaching.
Third, the saponification of caustic soda and few triglycerides causes an increase in refining loss. Therefore, the optimum operating conditions must be selected to obtain the highest yield of the finished product. The following table is the requirement for the acid value in end product of the common oil deacidification section:
| Oil grade or type | Acid value/mg·KOH/g |
| Edible fried oil, sesame oil, secondary rapeseed oil | ≤5.0 |
| Edible flaxseed oil, most secondary edible vegetable oil | ≤4.0 |
| Sesame oil | ≤3.0 |
| Secondary edible lard | ≤1.5 |
| First-grade vegetable oil and lard, shortening, margarine, edible hydrogenated oil | ≤1.0 |
| Edible vegetable oil | ≤0.6 |
| Senior cooking oil, the U. S. soybean oil, Japan reconcile oil | ≤0.5 |
| Salad oil, Japanese refined lard, the U. S. soybean salad oil | ≤0.3 |
| Japanese refined vegetable oil, refined reconcile oil | ≤0.2 |
| Japanese edible plant salad oil, reconcile salad oil | ≤0.15 |











